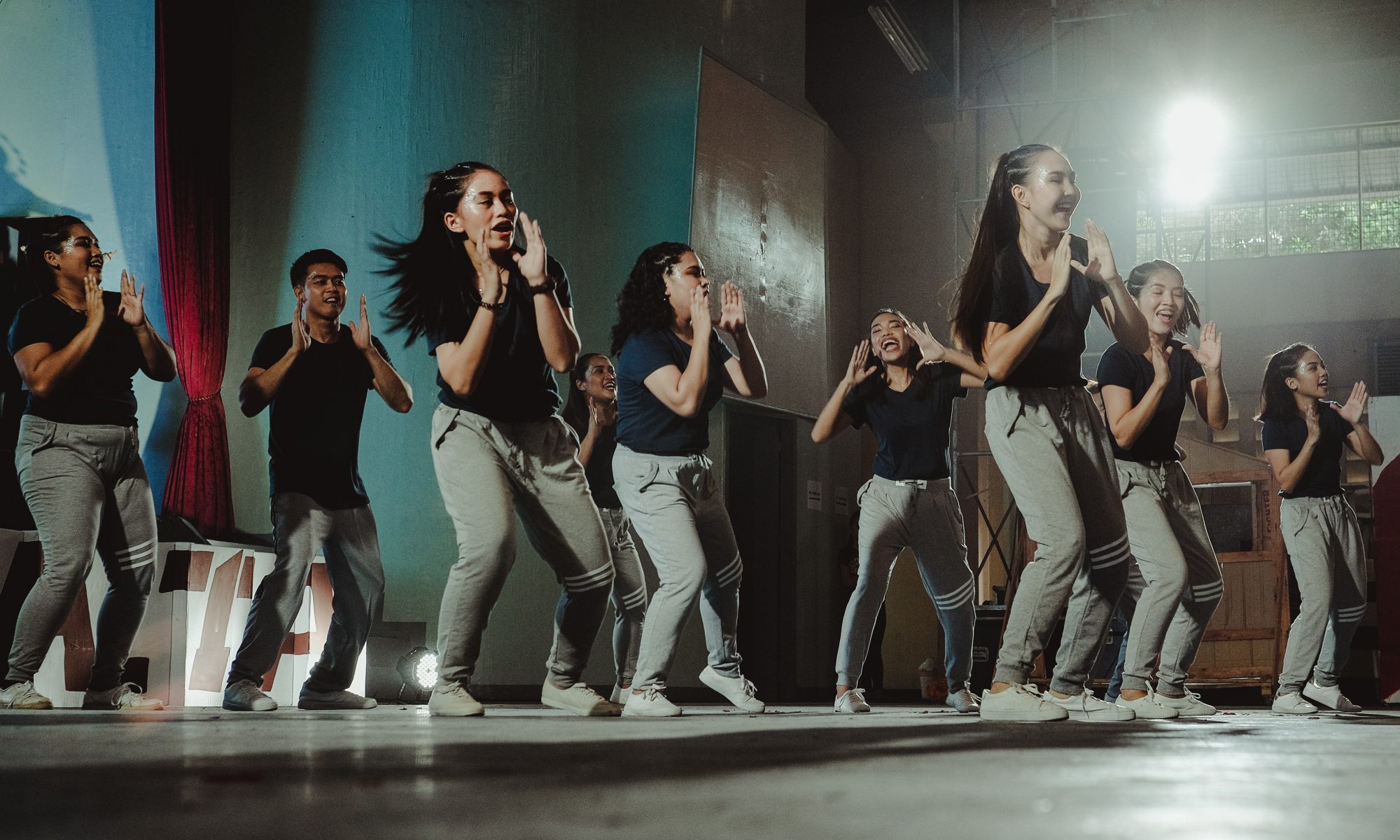“Within the field of deepfakes, or ‘synthetic media’ as researchers call it, much of the attention has been focused on fake faces potentially wreaking havoc on political reality, as well as other deep learning algorithms that can, for instance, mimic a person’s writing style and voice. But yet another branch of synthetic media technology is fast evolving: full body deepfakes.” (Fast Company, 21 September 2019) Last year, researchers from the University of California Berkeley demonstrated in an impressive way how deep learning can be used to transfer dance moves from a professional onto the bodies of amateurs. Also in 2018, a team from the University of Heidelberg published a paper on teaching machines to realistically render human movements. And in spring of this year, a Japanese company developed an AI that can generate whole body models of nonexistent persons. “While it’s clear that full body deepfakes have interesting commercial applications, like deepfake dancing apps or in fields like athletics and biomedical research, malicious use cases are an increasing concern amid today’s polarized political climate riven by disinformation and fake news.” (Fast Company, 21 September 2019) Was anyone really in this area, did he or she really take part in a demonstration and throw stones? In the future you won’t know for sure.
Robot Priests can Perform your Funeral
“Robot priests can bless you, advise you, and even perform your funeral” – this is the title of an article published in Vox on 9 September 2019. “A new priest named Mindar is holding forth at Kodaiji, a 400-year-old Buddhist temple in Kyoto, Japan. Like other clergy members, this priest can deliver sermons and move around to interface with worshippers. But Mindar comes with some … unusual traits. A body made of aluminum and silicone, for starters.” (Vox, 9 September 2019) The robot looks like Kannon, the Buddhist deity of mercy. According to Vox, it is an attempt to reignite people’s passion for their faith in a country where religious affiliation is on the decline. “For now, Mindar is not AI-powered. It just recites the same preprogrammed sermon about the Heart Sutra over and over. But the robot’s creators say they plan to give it machine-learning capabilities that’ll enable it to tailor feedback to worshippers’ specific spiritual and ethical problems.” (Vox, 9 September 2019) There is hope that the robot will not bring people back to faith, but rather enthuse them for the knowledge of science – the science that created Mindar.
Pepper’s New Job
SoftBank Robotics has announced that it will operate a cafe in Tokyo. The humanoid robot Pepper is to play a major role in this. But people will not disappear. They will of course be guests, but also, as in the traditional establishments of this kind, waitresses and waiters. At least that’s what ZDNET reports. “The cafe, called Pepper Parlor, will utilise both human and robot staff to serve customers, and marks the company’s first time operating a restaurant or cafe.” (ZDNET, 13 September 2019) According to SoftBank Robotics, the aim is “to create a space where people can easily experience the coexistence of people and robots and enjoy the evolution of robots and the future of living with robots”. “We want to make robots not only for convenience and efficiency, but also to expand the possibilities of people and bring happiness.” (ZDNET, 13 September 2019) This opens up new career opportunities for the little robot, which recognizes and shows emotions, and which listens and talks and is programmed to give high-fives. It has long since left its family’s lap, it can be found in shopping malls and nursing homes. Now it will be serving waffles in a cafe in Tokyo.
Ethics in AI for Kids and Teens
In summer 2019, Blakeley Payne ran a very special course at MIT. According to an article in Quartz magazine, the graduate student had created an AI ethics curriculum to make kids and teens aware of how AI systems mediate their everyday lives. “By starting early, she hopes the kids will become more conscious of how AI is designed and how it can manipulate them. These lessons also help prepare them for the jobs of the future, and potentially become AI designers rather than just consumers.” (Quartz, 4 September 2019) Not everyone is convinced that artificial intelligence is the right topic for kids and teens. “Some argue that developing kindness, citizenship, or even a foreign language might serve students better than learning AI systems that could be outdated by the time they graduate. But Payne sees middle school as a unique time to start kids understanding the world they live in: it’s around ages 10 to 14 year that kids start to experience higher-level thoughts and deal with complex moral reasoning. And most of them have smartphones loaded with all sorts of AI.” (Quartz, 4 September 2019) There is no doubt that the MIT course could be a role model for schools around the world. The renowned university once again seems to be setting new standards.
Permanent Record
The whistleblower Edward Snowden spoke to the Guardian about his new life and concerns for the future. The reason for the two-hour interview was his book “Permanent Record”, which will be published on 17 September 2019. “In his book, Snowden describes in detail for the first time his background, and what led him to leak details of the secret programmes being run by the US National Security Agency (NSA) and the UK’s secret communication headquarters, GCHQ.” (Guardian, 13 September 2019) According to the Guardian, Snowden said: “The greatest danger still lies ahead, with the refinement of artificial intelligence capabilities, such as facial and pattern recognition.” (Guardian, 13 September 2019) The number of public appearances by and interviews with him is rather manageable. On 7 September 2016, the movie “Snowden” was shown as a preview in the Cinéma Vendôme in Brussels. Jan Philipp Albrecht, Member of the European Parliament, invited Viviane Reding, the Luxembourg politician and journalist, and authors and scientists such as Yvonne Hofstetter and Oliver Bendel. After the preview, Edward Snowden was connected to the participants via videoconferencing for almost three quarters of an hour.
The New Dangers of Face Recognition
The dangers of face recognition are discussed more and more. A new initiative is aimed at banning the use of technology to monitor the American population. The AI Now Institute already warned of the risks in 2018, as did Oliver Bendel. The ethicist had a particular use in mind. In the 21st century, face recognition is increasingly attempted to connect to the pseudoscience of physiognomy, which has its origins in ancient times. From the appearance of persons, a conclusion is drawn to their inner self, and attempts are made to identify character traits, personality traits and temperament, or political and sexual orientation. Biometrics plays a role in this concept. It was founded in the eighteenth century, when physiognomy under the lead of Johann Caspar Lavater had its dubious climax. In his paper “The Uncanny Return of Physiognomy”, Oliver Bendel elaborates the basic principles of this topic; selected projects from research and practice are presented and, from an ethical perspective, the possibilities of face recognition are subjected to fundamental critique in this context, including the above examples. The philosopher presented his paper on 27 March 2018 at Stanford University (“AI and Society: Ethics, Safety and Trustworthiness in Intelligent Agents”, AAAI 2018 Spring Symposium Series). The whole volume is available here.
Fighting Deepfakes with Deepfakes
A deepfake (or deep fake) is a picture or video created with the help of artificial intelligence that looks authentic but is not. Also the methods and techniques in this context are labeled with the term. Machine learning and especially deep learning are used. With deepfakes one wants to create objects of art and visual objects or means for discreditation, manipulation and propaganda. Politics and pornography are therefore closely interwoven with the phenomenon. According to Futurism, Facebook is teaming up with a consortium of Microsoft researchers and several prominent universities for a “Deepfake Detection Challenge”. “The idea is to build a data set, with the help of human user input, that’ll help neural networks detect what is and isn’t a deepfake. The end result, if all goes well, will be a system that can reliably fake videos online. Similar data sets already exist for object or speech recognition, but there isn’t one specifically made for detecting deepfakes yet.” (Futurism, 5 September 2019) The winning team will get a prize – presumably a higher sum of money. Facebook is investing a total of 10 million dollars in the competition.
Dialects and Accents as a Challenge for Voice Assistants
Voice assistants often have difficulties with dialects. This was already evident in the case of Siri in 2012. In German-speaking Switzerland, she did not always understand users. There is a similar problem in the UK. Alexa and other voice assistants have trouble understanding the accents there. According to the Guardian, the BBC is preparing to launch a rival to Amazon’s Alexa called Beeb (a nickname for the public service broadcaster, just like “Auntie”). “The voice assistant, which has been created by an in-house BBC team, will be launched next year, with a focus on enabling people to find their favourite programmes and interact with online services. While some US-developed products have struggled to understand strong regional accents, the BBC will … ask staff in offices around the UK to record their voices and make sure the software understands them.” (Guardian, 27 August 2019) Auntie has no plans to develop or offer a physical product such as Amazon’s Echo speaker or a Google Home device. Instead, the Beeb software will be built into the BBC online services. It remains to be seen whether this will solve all problems of comprehension.
An AI System for Multiple-choice Tests
According to the New York Times, the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence unveiled a new system that correctly answered more than 90 percent of the questions on an eighth-grade science test and more than 80 percent on a 12th-grade exam. Is it really a breakthrough for AI technology, as the title of the article claims? This is a subject of controversy among experts. The newspaper is optimistic: “The system, called Aristo, is an indication that in just the past several months researchers have made significant progress in developing A.I. that can understand languages and mimic the logic and decision-making of humans.” (NYT, 4 September 2019) Aristo was built for multiple-choice tests. “It took standard exams written for students in New York, though the Allen Institute removed all questions that included pictures and diagrams.” (NYT, 4 September 2019) Some questions could be answered by simple information retrieval. There are numerous systems that access Google and Wikipedia, including artifacts of machine ethics like LIEBOT and BESTBOT. But for the answers to other questions logical thinking was required. Perhaps Aristo is helping to abolish multiple-choice tests – not so much because it can solve them, but because they are often not effective.
Punch the Robot
Robots are repeatedly damaged or destroyed. The hitchBOT is a well-known example. But also the security robot K5 has become a victim of attacks several times. The latest case is described in the magazine Wired: “Every day for 10 months, Knightscope K5 patrolled the parking garage across the street from the city hall in Hayward, California. An autonomous security robot, it rolled around by itself, taking video and reading license plates. Locals had complained the garage was dangerous, but K5 seemed to be doing a good job restoring safety. Until the night of August 3, when a stranger came up to K5, knocked it down, and kicked it repeatedly, inflicting serious damage.” (Wired, 29 August 2019) The author investigates the question of whether one may attack robots. Of course you shouldn’t damage other people’s property. But what if the robot is a spy, a data collector, a profile creator? Digital self-defence (which exploits digital as well as analog possibilities) seems to be a proven tool not only in Hong Kong, but also in the US and Europe. The rights of robots that some demand cannot be a serious problem. Robots do not have rights. They feel nothing, they do not suffer, they have no consciousness. “So punch the robot, I tell you! Test the strength of your sociopolitical convictions on this lunk of inorganic matter!” (Wired, 29 August 2019)