On May 28, 2025, the “Proceedings of the 2025 AAAI Spring Symposium Series” (Vol. 5 No. 1) were published. Oliver Bendel was involved in two papers at the symposium “Human-Compatible AI for Well-being: Harnessing Potential of GenAI for AI-Powered Science”. The paper “Revisiting the Trolley Problem for AI: Biases and Stereotypes in Large Language Models and their Impact on Ethical Decision-Making” by Sahan Hatemo, Christof Weickhardt, Luca Gisler, and Oliver Bendel is summarized as follows: “The trolley problem has long served as a lens for exploring moral decision-making, now gaining renewed significance in the context of artificial intelligence (AI). This study investigates ethical reasoning in three open-source large language models (LLMs) – LLaMA, Mistral and Qwen – through variants of the trolley problem. By introducing demographic prompts (age, nationality and gender) into three scenarios (switch, loop and footbridge), we systematically evaluate LLM responses against human survey data from the Moral Machine experiment. Our findings reveal notable differences: Mistral exhibits a consistent tendency to over-intervene, while Qwen chooses to intervene less and LLaMA balances between the two. Notably, demographic attributes, particularly nationality, significantly influence LLM decisions, exposing potential biases in AI ethical reasoning. These insights underscore the necessity of refining LLMs to ensure fairness and ethical alignment, leading the way for more trustworthy AI systems.” The renowned and traditional conference took place from March 31 to April 2, 2025 in San Francisco. The proceedings are available at ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI-SS/issue/view/654.
Miss Tammy in the AAAI Proceedings
On May 28, 2025, the “Proceedings of the 2025 AAAI Spring Symposium Series” (Vol. 5 No. 1) were published. Oliver Bendel was involved in two papers at the symposium “Human-Compatible AI for Well-being: Harnessing Potential of GenAI for AI-Powered Science”. The paper “Miss Tammy as a Use Case for Moral Prompt Engineering” by Myriam Rellstab and Oliver Bendel is summarized as follows: “This paper describes an LLM-based chatbot as a use case for moral prompt engineering. Miss Tammy, as it is called, was created between February 2024 and February 2025 at the FHNW School of Business as a custom GPT. Different types of prompt engineering were used. In addition, RAG was applied by building a knowledge base with a collection of netiquettes. These usually guide the behavior of users in communities but also seem to be useful to control the actions of chatbots and make them competent in relation to the behavior of humans. The tests with pupils aged between 14 and 16 showed that the custom GPT had significant advantages over the standard GPT-4o model in terms of politeness, appropriateness, and clarity. It is suitable for de-escalating conflicts and steering dialogues in the right direction. It can therefore contribute to users’ well-being and is a step forward in human-compatible AI.” The renowned and traditional conference took place from March 31 to April 2, 2025 in San Francisco. The proceedings are available at ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI-SS/issue/view/654.
Robots, Chatbots, and Voice Assistants
The GROUND workshop (advancing GROup UNderstanding and robots‘ aDaptive behavior) is back for its third edition and will take place on June 30, 2025, as part of the IAS 19 Conference in Genoa, Italy. The keynote speeches will be given by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel, FHNW School of Business, and Prof. Dr. Silvia Rossi, University of Naples. The talk by the technology philosopher and business information scientist from Zurich entitled “Robots, chatbots, and voice assistants in the classroom” is summarized as follows on the Ground website: “Chatbots, voice assistants, and robots – both programmable machines and social robots – have been used in learning for decades. Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel from the FHNW School of Business in Switzerland presents his own projects from 15 years. Some of his chatbots and voice assistants, such as GOODBOT, BESTBOT, and SPACE THEA, recognized user problems and responded appropriately. They showed empathy and emotion. Pepper was used as an educational application for children with diabetes, and Alpha Mini as an educational application for elementary schools. Chatbots for dead, endangered, and extinct languages such as @ve, @llegra, and kAIxo can be integrated into learning environments for all ages. Today, the technology philosopher and information systems expert mainly uses GPTs such as Social Robotics Girl and Digital Ethics Girl in his courses. They can receive and answer questions from several students at the same time, even if they are asked in different languages. They are specialists in their field thanks to prompt engineering and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). In his talk, Oliver Bendel will ask how chatbots, voice assistants, and social robots will be designed as adaptive systems for multi-user settings in the future. These capabilities are especially important in the classroom.” Further information is available at ground-hri.github.io/workshop/.
ICSR 2025 Workshops
The ICSR is one of the leading conferences for social robotics worldwide. The 17th edition will take place from 10 to 12 September 2025 in Naples, Italy. As part of the program, the conference welcomes proposals for workshops that provide a platform for in-depth discussion, exchange of knowledge, and community engagement around current topics in social robotics. The organizers are especially interested in workshops that promote dialogue between established researchers and early-career scientists, supporting a dynamic and inclusive research environment. The deadline for submitting workshop proposals is June 4, 2025. Notifications of acceptance will be sent by July 1, 2025. All details and the submission portal can be found at the following link: icsr2025.eu/ss-ws-proposal … ICSR 2025 offers an opportunity to help shape the future of social robotics through collaborative and forward-looking workshop initiatives.
GROUND Workshop in Genoa
The GROUND workshop (advancing GROup UNderstanding and robots’ aDaptive behavior) is back for its third edition and will take place on June 30, 2025, as part of the IAS 19 Conference in Genoa, Italy. This full-day event focuses on robotics in multiparty scenarios and human-robot interaction in group settings. It offers a unique platform for researchers and practitioners to share ideas, explore new approaches, and connect with a passionate community working at the intersection of social interaction and robotics. Participants can look forward to inspiring keynotes and talks by Prof. Dr. Silvia Rossi, Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel, and Dr. Isabel Neto, along with a hands-on tutorial led by Lorenzo Ferrini. The workshop invites short contributions (2–4 pages plus references) that present innovative strategies for advancing group-robot interaction. Key dates to keep in mind: the submission deadline is May 31, 2025; notifications of acceptance will be sent out on June 17, and the final camera-ready papers are due by June 22. For more information, visit the workshop website, the IAS-19 conference page, or go directly to the submission portal. Questions can be directed to: groundworkshop@gmail.com.
Intelligens. Natural. Artificial. Collective.
At the 19th Architecture Biennale in Venice (Biennale Architettura 2025) with the title “Intelligens. Natural. Artificial. Collective.”, robots play an important role. This is reported by several media, such as The Architect’s Newspaper. “Robots Falling from the Sky” is an installation in which robots appear to fall from the sky and interact with their surroundings. Another robot demonstrates its musical abilities by playing a handpan, a brass instrument. One is reminded of Henri-Louis Jaquet-Droz’s 18th century musician, who preferred a keyboard instrument. A robotic arm from ABB assists two Bhutanese craftsmen in working on a beam. For safety reasons, according to The Architect’s Newspaper, live carving with a drill was not permitted. The problem is not the two artisans, but the visitors. The Biennale is always dedicated to technical and futuristic themes. In 2021, the Architecture Biennale focused on cyborgs and transhumanists, among other things. In 2024, the art biennial featured a quasi-hologram and a spaceship-like installation. The Biennale runs from May 10 to November 23, 2025 at various venues in and near Venice, including the Giardini della Biennale, the Arsenale di Venezia, and the Forte Marghera in Mestre. Further information and the full program can be found at www.labiennale.org/en/architecture/2025 (Photo: Biennale Arte 2024).
ICSR Deadlines Extended One Last Time
The ICSR is one of the leading conferences for social robotics worldwide. The 17th edition will take place from 10 to 12 September 2025 in Naples, Italy. The deadline for submissions has been extended one last time. Full papers should consist of 11 pages of body text plus references as appropriate. The most important conferences dates are: Full Paper Submission: May 9th, 2025; Full Paper Notification: June 13th, 2025; Camera-ready: June 30th, 2025; Paper Presentation Days at ICSR’25: September 11th and 12th, 2025. All dates – including the deadlines for the submission of short papers and special session papers – are listed on the website. “The conference theme, ‘Emotivation at the Core: Empowering Social Robots to Inspire and Connect,’ highlights the essential role of ‘Emotivation’ in social robotics. Emotivation captures the synergy between emotion and motivation, where emotions trigger and sustain motivation during interactions. In social robotics, this concept is key to building trust, fostering empathy, and supporting decision-making by enabling robots to respond sensitively to human emotions, inspiring engagement and action.” (Website ICSR) Participants will meet for two days at the Parthenope University of Naples and for the third day at the Città della Scienza conference center. All buildings and rooms are also listed on the website. The PDF of the CfP can be downloaded here.
Manipulated Chatbots as Munchausen Machines
In 2013, Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel came up with the idea for his LIEBOT, also known as Lügenbot. On September 11, 2013, he published an article titled “Der Lügenbot und andere Münchhausen-Maschinen” in the magazine CyberPress. More articles and contributions followed until a prototype was implemented in 2016. Kevin Schwegler, then a student of the philosopher of technology, was responsible for this work. He developed a chatbot that transformed truthful statements into false ones using seven different strategies. In the summer of 2016, for example, LIEBOT claimed that Donald Trump was the President of the United States. To make this statement, it had used information from Yahoo in a multi-step process. The results of the project were documented in a paper titled “Towards Kant Machines” and presented in March 2017 at the AAAI Spring Symposia at Stanford University. One might argue that LIEBOT does not have intentions of its own and therefore does not lie in the strict sense. However, this intent was programmed into it. In a way, it lies on behalf of its creators. With this project, Oliver Bendel wanted to demonstrate that it is possible to build dialogue systems capable of spreading falsehoods. Today, such systems seem to be omnipresent in the form of LLMs. However, one has to look closely to discern the differences. In his book “300 Keywords Generative KI”, Oliver Bendel writes: “Hallucinating machines do not necessarily qualify as Munchausen machines in the strict sense, since there is no intent – or at least intent can hardly be proven.” Manipulated LLM-based chatbots, on the other hand, come very close to LIEBOT. ChatGPT and similar systems pursue a political agenda and exhibit an ideological tendency.
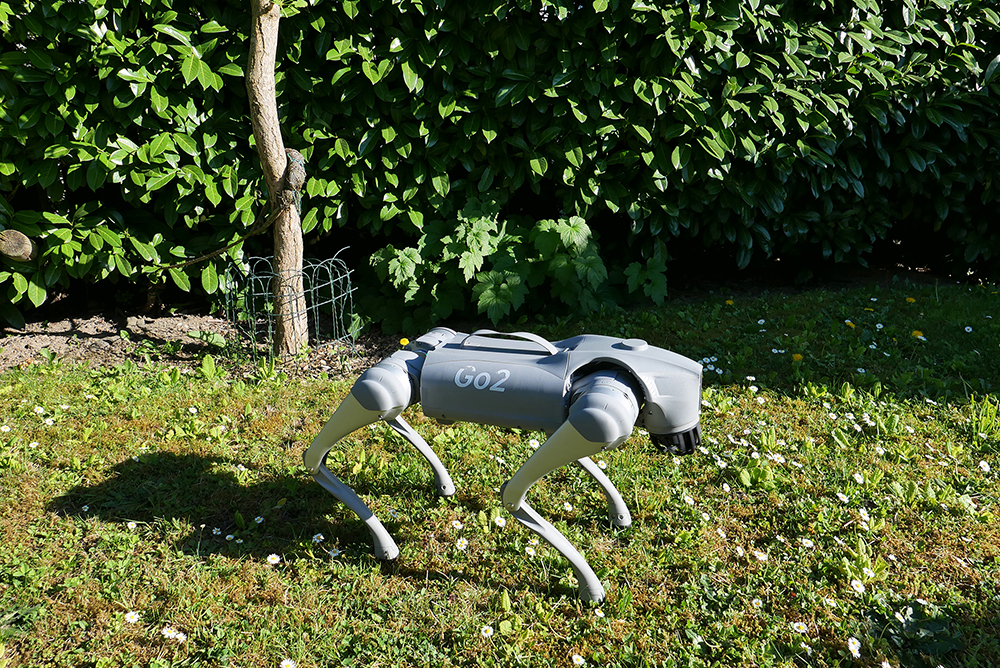
The Robodog Project
Robotic quadrupeds – often referred to as robot dogs – are becoming more and more widespread. As a result, they will increasingly encounter real dogs. The question is how to design and construct the robot in such a way that the animals do not overreact and neither robots nor animals or bystanders are harmed in any way. As part of “The Robodog Project”, smaller dogs are to be confronted with the walking, running and jumping Unitree Go2 from Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel’s private Social Robots Lab. The plan is to visit controllable environments such as dog training grounds and arrange meetings and discussions with dog owners. The results will lead to suggestions for design and control. Robot enhancement can also play a role. For example, robot enthusiasts have used a 3D printer to produce cartoonish heads for the Unitree Go2, giving it a completely different look. The project – also known as “Bao Meets Pluto” after the pet name of the robotic four-legged friend and the Disney character – was launched at the FHNW School of Business at the end of March 2025. It is part of Oliver Bendel’s research in the field of animal-machine interaction (AMI). Selina Rohr, who is writing her Bachelor’s thesis on the topic, has been recruited as a member of the team. She met Bao at a get-together at the end of April 2025 and let it run and jump around the room.