The VISUAL project will be launched in March 2025 at the FHNW School of Business. It was initiated by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel. VISUAL stands for “Virtual Inclusive Safaris for Unique Adventures and Learning”. There are webcams all over the world showing wild animals. Sighted people can use them to go on photo safaris from the comfort of their sofa. Blind and visually impaired people are at a disadvantage. As part of inclusive AI – a movement that includes apps like Be My Eyes with the Be My AI feature – a solution is to be found for them. The project aims to develop a prototype by August 2025 that will allow blind and visually impaired people to have webcam images of wildlife described to them. The system takes regular snapshots of the videos and analyzes and evaluates them using a multimodal LLM. It presents the results ini spoken language via an integrated text-to-speech engine. As a byproduct, poaching, bush and forest fires, and other events can be detected. The project is likely to be one of the first to combine inclusive AI with new approaches of animal-computer interaction (ACI).
Biases and Stereotypes in LLMs
The paper “Revisiting the Trolley Problem for AI: Biases and Stereotypes in Large Language Models and their Impact on Ethical Decision-Making” by Sahan Hatemo, Christof Weickhardt, Luca Gisler (FHNW School of Computer Science), and Oliver Bendel (FHNW School of Business) was accepted at the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposium “Human-Compatible AI for Well-being: Harnessing Potential of GenAI for AI-Powered Science”. A year ago, Sahan Hatemo had already dedicated himself to the topic of “ETHICAL DECISION MAKING OF AI: An Investigation Using a Stereotyped Persona Approach in the Trolley Problem” in a so-called mini-challenge in the Data Science degree program. His supervisor, Oliver Bendel, had told the other scientists about the idea at the AAAI 2025 Spring Symposium “Impact of GenAI on Social and Individual Well-being” at Stanford University. This led to a lively discussion. The student recruited two colleagues, Christof Weickhardt and Luca Gisler, and worked on the topic in a much more complex form in a so-called Challenge X. This time, three different open-source language models were applied to the trolley problem. In each case, personalities were created with nationality, gender, and age. In addition, the data was compared with that of the MIT Moral Machine project. Sahan Hatemo, Christof Weickhardt, and Luca Gisler will present their results at the end of March or beginning of April 2025 in San Francisco, the venue of this year’s event.
Special Sessions at ICSR 2025
ICSR’25 allows for special sessions on topics of particular interest to attendees. The goal is to complement the regular program with new and emerging topics of interest in social robotics. Proposals will be evaluated on a rolling basis until the deadline below, and organizers will be notified of the outcome. Once accepted, the invited session will be published on the ICRS website along with an invited session code to be used at the time of paper submission. Special session papers will go through the same review process as regular papers and will be published in the same way. Papers should be submitted as PDF documents of no more than 3-4 pages. More information is available at icsr2025.eu/ss-ws-proposal/.
A Video About the ICSR 2023
ICSR is one of the leading conferences for social robotics worldwide. The 17th edition will take place from 10 to 12 September 2025 in Naples, Italy. Participants will meet for two days at the Parthenope University of Naples and for the third day at the Città della Scienza conference center. In 2023, the conference took place in Doha, Qatar. A video on YouTube by Hooman Samani provides insights into the presentations and events: www.youtube.com/watch?v=MtgM8pTPw8c … It not only shows that numerous top-class presentations take place, but also that the members of the community are highly motivated and have a lot of fun. The high level of internationality and diversity of the conference should also be emphasized. The conference website of ICSR 2025 is online since January: icsr2025.eu.
A Video About the ICSR 2024
ICSR is one of the leading conferences for social robotics worldwide. The 17th edition will take place from 10 to 12 September 2025 in Naples, Italy. Participants will meet for two days at the Parthenope University of Naples and for the third day at the Città della Scienza conference center. In 2024, the conference took place in Odense, Denmark. A video on YouTube by Hooman Samani provides insights into the presentations and events: www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xj6p2yguYBk … It not only shows that numerous top-class presentations take place, but also that the members of the community are highly motivated and have a lot of fun. The high level of internationality and diversity of the conference should also be emphasized. The conference website of ICSR 2025 is online since January: icsr2025.eu.
Cute little AIBI
Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel’s privately funded Social Robots Lab has been home to little AIBI since January 2025. It comes from the Chinese company LivingAI. Other robots and figures in the Social Robots Lab are Cupboo AI Robotic Pet aka Boo Boo, Unitree Go2, Alpha Mini, Cozmo, Vector, Furby, Tamagotchi, and Hugvie. HUGGIE was dismantled at the beginning of 2025 and given to a student project in which the robot laughs with a synthetic or natural voice. NAO and Pepper visit the lab and the elective module on social robots from time to time. AIBI has various sensors, a camera, and three microphones. It understands voice commands. For more complex questions, it connects to ChatGPT. The face consists of a display in which it can show animated eyes and animated scenes of all kinds. It stands on a platform that allows it to rotate 360 degrees. It can also turn its head freely. Similar to Cozmo, it emits numerous sounds and tries to attract the user’s attention in this and other ways. Thanks to its magnets, it can be attached to the fridge and other metal surfaces, as well as to an included necklace, transforming it into a wearable. It also transforms with accessories, for example into a cat. Robot enhancement is therefore included and supplied by the company.
The ICSR 2025 Website is Now Online
The ICSR is one of the leading conferences for social robotics worldwide. The 17th edition will take place from 10 to 12 September 2025 in Naples, Italy. The conference website is now online: icsr2025.eu. “The conference theme, ‘Emotivation at the Core: Empowering Social Robots to Inspire and Connect,’ highlights the essential role of ‘Emotivation’ in social robotics. Emotivation captures the synergy between emotion and motivation, where emotions trigger and sustain motivation during interactions. In social robotics, this concept is key to building trust, fostering empathy, and supporting decision-making by enabling robots to respond sensitively to human emotions, inspiring engagement and action.” (Website ICSR) The most important conferences dates are: Full Paper Submission: March 28th, 2025; Full Paper Notification: May 9th, 2025; Camera-ready: June 30th, 2025; Paper Presentation Days at ICSR’25: September 11th and 12th, 2025. All dates are also listed on the website. Participants will meet for two days at the Parthenope University of Naples and for the third day at the Città della Scienza conference center. All buildings and rooms are also listed on the website. Be part of this excellent conference (Photo: ICSR)!
22 Chatbots and Voice Assistants
Since 2013, Oliver Bendel has developed 22 chatbots and voice assistants together with his students or colleagues. They can be divided into three categories. The first are moral and immoral chatbots (i.e., forms of moral machines) and empathic voice assistants. The second are chatbots (some with voice output) for dead, endangered, or extinct languages and idioms. The third are pedagogical chatbots and chatbots that give recommendations and advice. Some of the projects lasted between four and six months. Most of the GPTs were created in just a few hours. Exceptions are Miss Tammy and Animal Whisperer, which took several months to build with the help of prompt engineering and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Articles and book chapters have been published on many of the projects. The names of the developers can be found in these. A few chatbots made it into the media, such as GOODBOT (for which the preparatory work began in 2012), LÜGENBOT aka LIEBOT, and @llegra.
Cleop@tr@ Visits the Karnak Temple
Cleop@tr@ was invented by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel in May 2024. It is a GPT that specializes in Egyptian. It is also familiar with the culture and history of ancient Egypt. Since 2012, the technology philosopher and information systems specialist has been building chatbots and voice assistants – partly with his students and partly on his own. These have been discussed by the media and found interesting by NASA. Under his supervision, Karim N’diaye developed the chatbot @ve for Latin, Dalil Jabou the voice-enhanced chatbot @llegra for Vallader, and Nicolas Lluis Araya the voice-enhanced chatbot kAIxo for Basque. For some time now, he has been testing the reach of GPTs for endangered languages such as Irish, Maori, and Basque. He is also investigating the potential for extinct languages such as Egyptian (Cleop@tr@) and Akkadian (H@mmur@pi). The GPTs do not readily communicate in hieroglyphics and cuneiform, but they can certainly represent and explain signs of visual languages. It is even possible to enter entire sentences and then ask how they can be improved or what they mean. In December 2024, Oliver Bendel tested his Cleop@tr@ in the Karnak Temple in Luxor. She was able to provide coherent explanations and translations for several inscriptions on columns and walls. However, further tests also revealed clear errors. Ultimately, Egyptologists will have to assess how reliable it is.
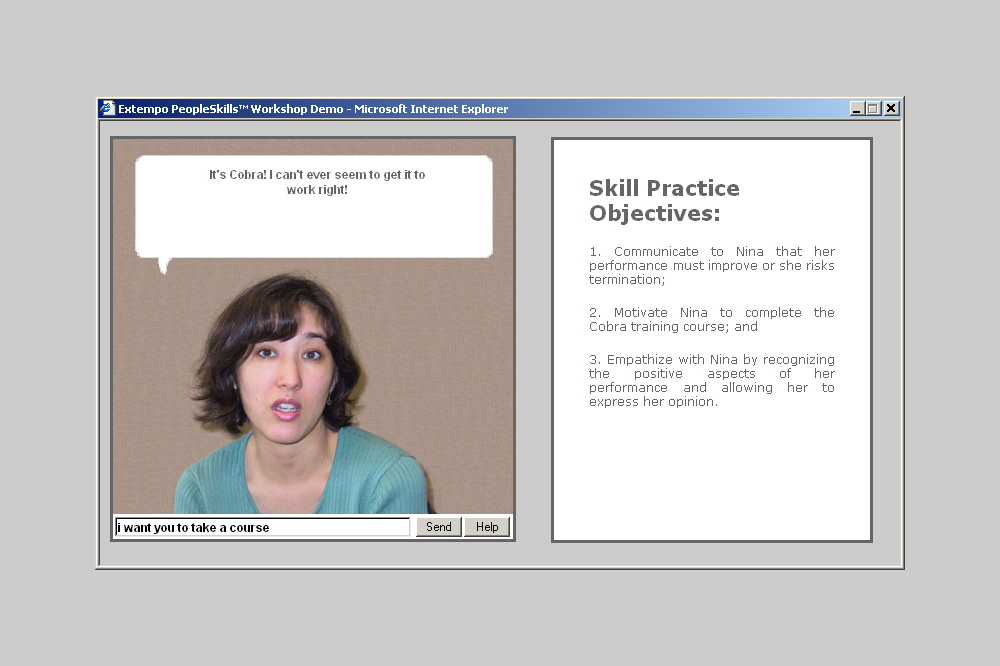
Role Player Nina
Around the turn of the millennium, there were already numerous pedagogical agents, i.e., chatbots, voice assistants, and early social robots in learning environments. Names such as Virtual Learning Companions (VLCs) were also commonly used for the purely virtual versions. One of the companies that was ahead of its time was Extempo Systems, Inc. based in Redwood City, California. The company had evolved out of the Stanford Engineering School and designed and developed commercial agents for entertainment, business, and education: “Extempo makes e-learning products that help corporate employees perfect their people skills. The company’s approach allows every learner to achieve mastery of the people skills they need for effective management, teamwork, sales, customer service, and other critical business functions. Extempo’s products give learners authentic practice in a variety of job-specific conversational role-plays, along with expert individualized coaching throughout the learning process.” (Extempo Systems) One example was the virtual Nina, with whom you could communicate and who you were supposed to motivate to behave in a certain way. It wasn’t just the functionality that was impressive at the time, but also the design of the characters.