Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel will host the next ACI Conference, marking the first time the event comes to continental Europe as it convenes on the FHNW campus in Brugg-Windisch, Switzerland, from 2-5 December 2026. Building on a tradition that has taken the community from Glasgow to North Carolina, Newcastle, Bloomington, Milton Keynes, Haifa and Atlanta, this edition continues the conference’s role as the premier venue for advancing Animal-Computer Interaction. As the field grows, researchers and practitioners explore how technology shapes animals’ lives, wellbeing, cognition and social dynamics while developing animal-centered systems and methods that embrace multispecies perspectives. The conference maintains its commitment to interdisciplinary collaboration across biology, technology and cultural studies, supporting work that seeks to design ethically grounded, welfare-enhancing and inclusive technological futures for all animals, humans included. The proceedings will be published in a volume of a renowned organization. The official conference website will go live in January 2026. Information on previous ACI conferences is available at www.aciconf.org.
Fundamentals of Animal-Machine Interaction
“Just.Us + Animal Welfare” is a lecture series organized by Department 10 Veterinary Medicine to promote animal welfare at Justus Liebig University Giessen. On November 12, 2025, Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel gave a lecture on “Bao meets Pluto: Grundlagen und Beispiele der Tier-Maschine-Interaktion” (“Bao meets Pluto: Fundamentals and examples of animal-machine interaction”). Animal-machine interaction deals with the encounter and coexistence of animals and machines – from classic devices to vehicles, aircraft, and agricultural machinery to networked, autonomous robots and AI systems. The focus is on perception through sensors and senses, interaction and communication between animals and machines, and the question of how these encounters can be designed technically, organizationally, and ethically in such a way that risks for animals are reduced and potential for them and for humans is tapped. In his lecture, Oliver Bendel laid out the fundamentals of animal-machine interaction and described prototypes and projects. He also outlined what is possible and to be expected in this field of research in the coming years, for example in connection with robotic quadrupeds and bipeds. The online lecture was followed by 660 listeners. Further information is available at www.uni-giessen.de/de/fbz/zentren/icar3r/akademie/justus.
The Hippo in the Mud
On November 10, 2025, the article “There’s a Large Hippo Resting in the Mud” by Oliver Bendel and Doris Jovic was published introducing the VISUAL project. “VISUAL” stands for “Virtual Inclusive Safaris for Unique Adventures and Learning”. All over the world, there are webcams showing wild animals. Sighted people can use them to go on photo and video safaris comfortably from their sofas. Blind and visually impaired people are at a disadvantage here. As part of Inclusive AI, the project developed a prototype specifically for them. Public webcams around the world that are directed at wild animals are tapped. Users can choose between several habitats on land or in water. They can also select “Adult” or “Child” as a profile and choose a role (“Safari Adventurer”, “Field Scientist”, “Calm Observer”). When the live video is accessed, three screenshots are taken and combined into a bundle. This bundle is analyzed and evaluated by GPT-4o, an MLLM. The user then hears a spoken description of the scene and the activities. The project is likely one of the first to combine Inclusive AI with new approaches in Animal-Computer Interaction (ACI). The article was published in Wiley Industry News and can be accessed at: wileyindustrynews.com/en/contributions/theres-a-large-hippo-resting-in-the-mud. It should be noted that it is also available in German.
Decoding Animal Language with AI
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and bioacoustics have opened a unique opportunity to explore and decode animal communication. With the growing availability of bioacoustic data and sophisticated machine learning models, researchers are now in a position to make significant strides in understanding non-human animal languages. However, realizing this potential requires a deliberate integration of AI and ethology. The AI for Non-Human Animal Communication workshop at NeurIPS 2025 will focus on the challenges of processing complex bioacoustic data and interpreting animal signals. The workshop will feature keynote talks, a poster session, and a panel discussion, all aimed at advancing the use of AI to uncover the mysteries of animal communication and its implications for biodiversity and ecological conservation. The workshop is inviting submissions for short papers and proposals related to the use of AI in animal communication. Topics of interest include bioacoustics, multimodal learning, ecological monitoring, species-specific studies, and the ethical considerations of applying AI in animal research. Papers should present novel research, methodologies, or technologies in these areas, and will undergo a double-blind review process. The paper submission deadline is September 5, 2025, with notifications of acceptance by September 22, 2025. More information is available at aiforanimalcomms.org.
When Animals and Robots Meet
The volume “Animals, Ethics, and Engineering: Intersections and Implications”, edited by Rosalyn W. Berne, was published on 7 August 2025. The authors include Clara Mancini, Fiona French, Abraham Gibson, Nic Carey, Kurt Reymers, and Oliver Bendel. The title of Oliver Bendel’s contribution is “An Investigation into the Encounter Between Social Robots and Animals”. The abstract reads: “Increasingly, social robots and certain service robots encounter, whether this is planned or not, domestic, farm, or wild animals. They react differently, some interested, some disinterested, some lethargic, some panicked. Research needs to turn more to animal-robot relationships, and to work with engineers to design these relationships in ways that promote animal welfare and reduce animal suffering. This chapter is about social robots that are designed for animals, but also those that – for different, rather unpredictable reasons – meet, interact, and communicate with animals. It also considers animal-friendly machines that have emerged in the context of machine ethics. In the discussion section, the author explores the question of which of the presented robots are to be understood as social robots and what their differences are in their purpose and in their relationship to animals. In addition, social and ethical aspects are addressed.” The book was produced by Jenny Publishing and can be ordered via online stores.
Completion of the VISUAL Project
On July 31, 2025, the final presentation of the VISUAL project took place. The initiative was launched by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel from the University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland (FHNW). It was carried out by Doris Jovic, who is completing her Bachelor’s degree in Business Information Technology (BIT) in Basel. “VISUAL” stands for “Virtual Inclusive Safaris for Unique Adventures and Learning”. All over the world, there are webcams showing wild animals. Sighted individuals can use them to go on photo or video safaris from the comfort of their couches. However, blind and visually impaired people are at a disadvantage. As part of Inclusive AI, a prototype was developed specifically for them in this project. Public webcams around the world that are focused on wildlife are accessed. Users can choose between various habitats on land or in water. Additionally, they can select a profile – either “Adult” or “Child” – and a role such as “Safari Adventurer,” “Field Scientist”, or “Calm Observer”. When a live video is launched, three screenshots are taken and compiled into a bundle. This bundle is then analyzed and evaluated by GPT-4o, a multimodal large language model (MLLM). The user receives a spoken description of the scene and the activities. The needs of blind and visually impaired users were gathered through an accessible online survey, supported by FHNW staff member Artan Llugaxhija. The project is likely one of the first to combine Inclusive AI with new approaches from the field of Animal-Computer Interaction (ACI).
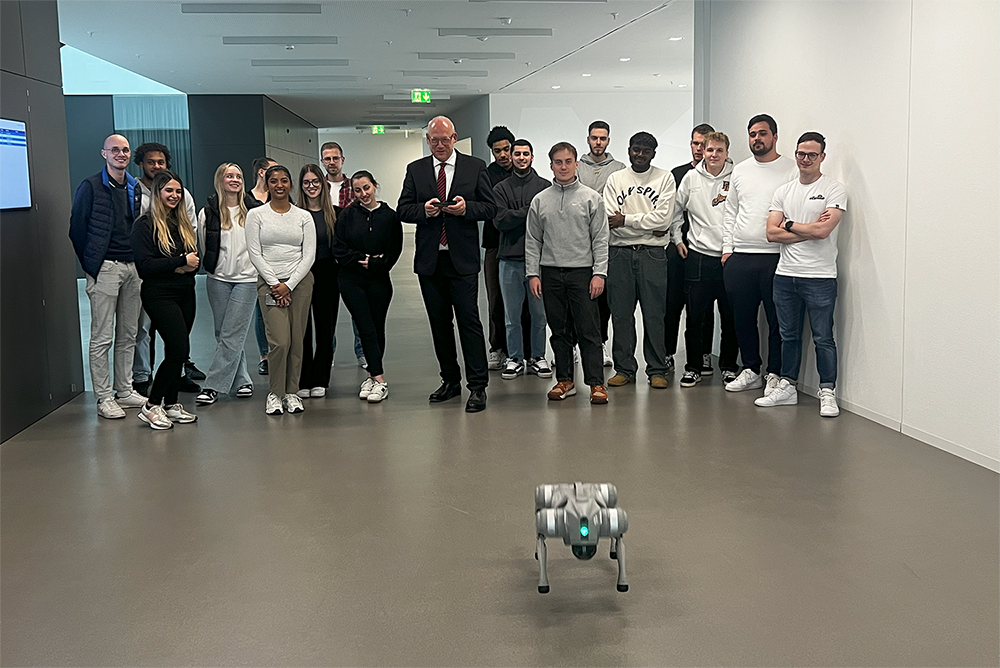
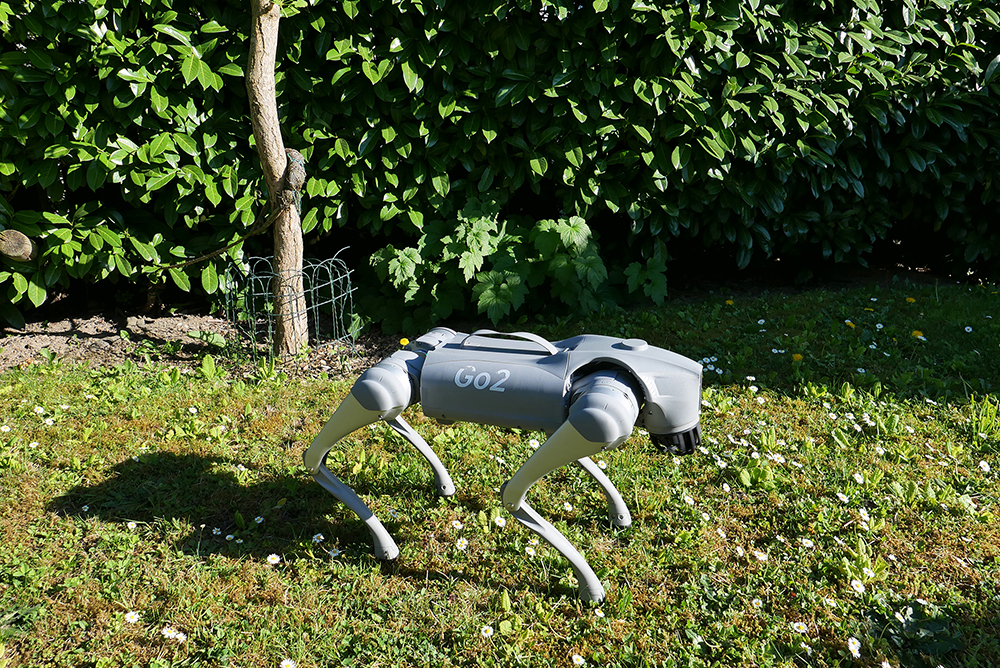
When the Robodog is Barked at
Animal-machine interaction (AMI) is a discipline or field of work that deals with the interaction between animals and machines. This is how Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel explains it in the Gabler Wirtschaftslexikon. It is primarily concerned with the design, evaluation, and implementation of complex machines and computer systems with which animals interact and which in turn interact and communicate with animals. There are close links to animal-computer interaction (ACI). Increasingly, the machine is a robot that is either remote-controlled or (partially) autonomous. In “The Robodog Project” (also known as “Bao Meets Pluto“), the encounters between robotic quadrupeds and small to medium-sized dogs are explored. The project collaborator is Selinar Rohr, who is writing her bachelor’s thesis in this context. The walking, running, and jumping Unitree Go2 from Oliver Bendel’s private Social Robots Lab is in its original state or is wearing a head made with a 3D printer provided by Norman Eskera. The project is being carried out at the FHNW School of Business and will end on August 12, 2025, after which the results will be presented to the community and, if possible, to the general public.
The Robodog Project
Robotic quadrupeds – often referred to as robot dogs – are becoming more and more widespread. As a result, they will increasingly encounter real dogs. The question is how to design and construct the robot in such a way that the animals do not overreact and neither robots nor animals or bystanders are harmed in any way. As part of “The Robodog Project”, smaller dogs are to be confronted with the walking, running and jumping Unitree Go2 from Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel’s private Social Robots Lab. The plan is to visit controllable environments such as dog training grounds and arrange meetings and discussions with dog owners. The results will lead to suggestions for design and control. Robot enhancement can also play a role. For example, robot enthusiasts have used a 3D printer to produce cartoonish heads for the Unitree Go2, giving it a completely different look. The project – also known as “Bao Meets Pluto” after the pet name of the robotic four-legged friend and the Disney character – was launched at the FHNW School of Business at the end of March 2025. It is part of Oliver Bendel’s research in the field of animal-machine interaction (AMI). Selina Rohr, who is writing her Bachelor’s thesis on the topic, has been recruited as a member of the team. She met Bao at a get-together at the end of April 2025 and let it run and jump around the room.
Start of the VISUAL Project
The kick-off meeting for the VISUAL project took place on March 20, 2025. It was initiated by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel from the FHNW School of Business. “VISUAL” stands for “Virtual Inclusive Safaris for Unique Adventures and Learning”. There are webcams all over the world that show wild animals. Sighted people can use them to go on a photo safari from the comfort of their sofa. Blind and visually impaired people are at a disadvantage. As part of Inclusive AI – an approach and a movement that also includes apps such as Be My Eyes with the Be My AI function – a solution is to be found for them. The aim of the project is to develop a prototype by August 2025 that enables blind and visually impaired people to have webcam images or videos of wild animals described to them. The system analyzes and evaluates them with the help of a multimodal LLM. It presents the results in spoken language via an integrated text-to-speech engine. As a by-product, poaching, bush and forest fires and other events can be detected. The project is likely to be one of the first to combine inclusive AI with new approaches to animal-computer interaction (ACI). Doris Jovic, who is completing her degree in BIT, has been recruited to work on the project.
13 Animal-Related Concepts and Artifacts
Since 2012, Oliver Bendel has developed 13 concepts and artifacts in the field of animal-computer interaction (ACI) or animal-machine interaction (AMI) together with his students. They can be divided into three categories. The first are animal- and nature-friendly concepts. The second are animal-friendly machines and systems (i.e., forms of moral machines). The third are animal-inspired machines and systems that replace the animals or bring them closer to you. Articles and book chapters have been published on many of the projects. The names of the developers can be found in these. A few prototypes made it into the media, such as LADYBIRD and HAPPY HEDGEHOG. Oliver Bendel repeatedly refers to Clara Mancini, the pioneer in the field of animal-computer interaction. Recently, ethicists such as Peter Singer have also turned their attention to the topic.