The initiative “Grundrechte für Primaten” (“Basic Rights for Primates”) went online with its website on April 30, 2021. The supporters demand the introduction of basic rights for non-human primates at cantonal constitutional level in Basel-Stadt. Among them are Simon Fankhauser (co-president Young Green Alliance), Dr. Charlotte E. Blattner (lawyer), Prof. Dr. Markus Wild (philosopher), Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel (ethicist and business information systems scientist), Jaël Malli (musician), and Dr. Colin Goldner (head of the Great Ape Project Germany). Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel goes particularly far in his requests: “I am for human rights for humans and for animal rights for animals. Basic rights such as the right to life and the right to physical integrity should go to all primates, but also to other mammals as well as reptiles and amphibians. The idea is not to protect animals from other animals, but from humans.” He combines animal ethics and animal welfare with machine ethics and develops animal-friendly machines with his teams. The initiative’s website can be reached at www.primaten-initiative.ch.
Robots that Spare Animals
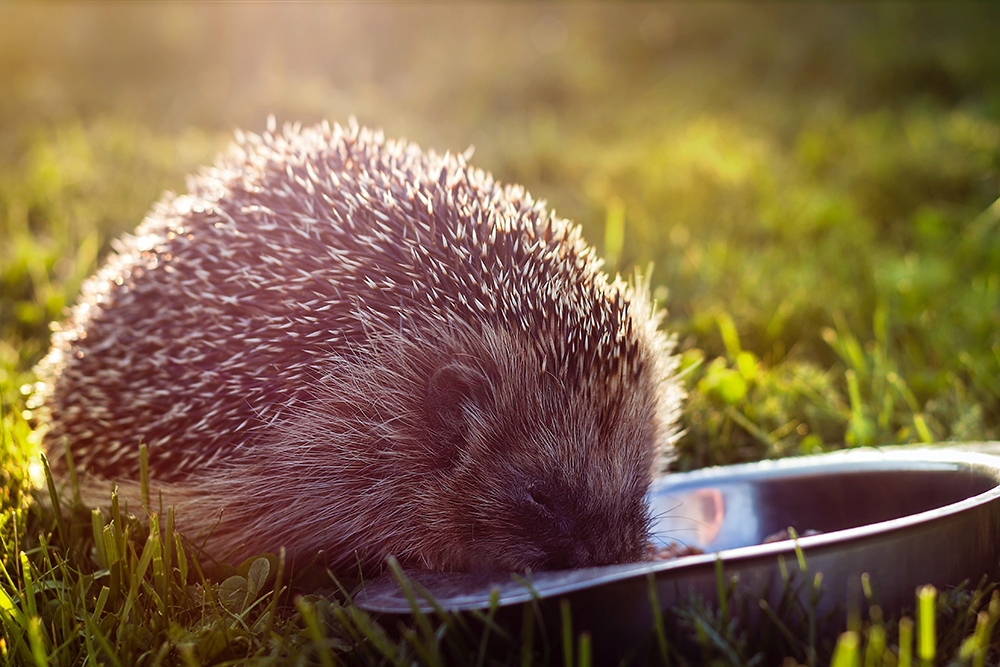
Semi-autonomous machines, autonomous machines and robots inhabit closed, semi-closed and open environments, more structured environments like the household or more unstructured environments like cultural landscapes or the wilderness. There they encounter domestic animals, farm animals, working animals, and wild animals. These creatures could be disturbed, displaced, injured, or killed by the machines. Within the context of machine ethics and social robotics, the School of Business FHNW developed several design studies and prototypes for animal-friendly machines, which can be understood as moral and social machines in the spirit of these disciplines. In 2019-20, a team led by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel developed a prototype robot lawnmower that can recognize hedgehogs, interrupt its work for them and thus protect them. Every year many of these animals die worldwide because of traditional service robots. HAPPY HEDGEHOG (HHH), as the invention is called, could be a solution to this problem. This article begins by providing an introduction to the background. Then it focuses on navigation (where the machine comes across certain objects that need to be recognized) and thermal and image recognition (with the help of machine learning) of the machine. It also presents obvious weaknesses and possible improvements. The results could be relevant for an industry that wants to market their products as animal-friendly machines. The paper “The HAPPY HEDGEHOG Project” is available here.
The Robot Called HAPPY HEDGEHOG
The paper “The HAPPY HEDGEHOG Project” by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel, Emanuel Graf and Kevin Bollier was accepted at the AAAI Spring Symposia 2021. The researchers will present it at the sub-conference “Machine Learning for Mobile Robot Navigation in the Wild” at the end of March. The project was conducted at the School of Business FHNW between June 2019 and January 2020. Emanuel Graf, Kevin Bollier, Michel Beugger and Vay Lien Chang developed a prototype of a lawn mowing robot in the context of machine ethics and social robotics, which stops its work as soon as it detects a hedgehog. HHH has a thermal imaging camera. When it encounters a warm object, it uses image recognition to investigate it further. At night, a lamp mounted on top helps. After training with hundreds of photos, HHH can quite accurately identify a hedgehog. With this artifact, the team provides a solution to a problem that frequently occurs in practice. Commercial robotic mowers repeatedly kill young hedgehogs in the dark. HAPPY HEDGEHOG could help to save them. The video on informationsethik.net shows it without disguise. The robot is in the tradition of LADYBIRD.
An Insect-size Microrobot
In their paper “Scaling down an insect-size microrobot, HAMR-VI into HAMR-Jr”, Kaushik Jayaram (Harvard Microrobotics Lab) and his co-authors present HAMR-Jr, a 22.5 mm, 320 mg quadrupedal microrobot. “With eight independently actuated degrees of freedom, HAMR-Jr is … the most mechanically dexterous legged robot at its scale and is capable of high-speed locomotion … at a variety of stride frequencies … using multiple gaits.” (Abstract) The scientists achieved this “using a design and fabrication process that is flexible, allowing scaling with minimum changes to our workflow”. They “further characterized HAMR-Jr’s open-loop locomotion and compared it with the larger scale HAMR-VI microrobot to demonstrate the effectiveness of scaling laws in predicting running performance” (Abstract) . The work is partially funded by the DARPA SHort Range Independent Microrobotic Platforms and the Department of Defense (DoD) through the National Defense Science & Engineering Graduate (NDSEG) Fellowship Program. There is no doubt that the military is interested in miniature robots that are as big as cockroaches. They are certainly just as interested in animal cyborgs that use cockroaches as the commercial RoboRoach. At least no animals will be harmed in the scientific project. The paper is available here.
A Robot Dog as Sheepdog
In May 2020 the media was interested in a video by Rocos showing a robot from Boston Dynamics trying to be a shepherd dog. You could see the artificial quadruped running towards a flock of sheep. “Now, it’s clear that the video is mostly a fun teaser rather than a serious claim by Rocos (or Boston Dynamics) that robots will soon be replacing sheepdogs.” (The Verge, 22 May 2020) According to the magazine, it does invite a tantalizing question: if that did happen, “how well would the robots fare” (The Verge, 22 May 2020)? “Terrible”, is the straight answer of sheep farmer and author James Rebanks. “The robot might be an amazing tool for lots of things but it is worthless and unwanted as a sheepdog …” (The Verge, 22 May 2020) However, the profession of shepherd is not everywhere in the world the dream of all boys and girls, and shepherd dogs do not fall from the sky. It is also not clear whether there is a big difference for the sheep and how positively or negatively they react to the machine. It is just as unclear whether lambs that have never met real dogs would be comfortable with it. This would have to be researched in animal psychology and social robotics and in disciplines such as animal-machine interaction, which are still in their infancy. Only then would one know whether the shepherd interviewed by the magazine is right.
Towards Animal-machine Interaction
Animal-machine interaction (AMI) and animal-computer interaction (ACI) are increasingly important research areas. For years, semi-autonomous and autonomous machines have been multiplying all over the world, not only in factories, but also in outdoor areas and in households. Robots in agriculture and service robots, some with artificial intelligence, encounter wild animals, farm animals and pets. Jackie Snow, who writes for New York Times, National Geographic, and Wall Street Journal, talked to several people on the subject last year. In an article for Fast Company, she quoted the ethicists Oliver Bendel (“Handbuch Maschinenethik”) and Peter Singer (“Animal Liberation”). Clara Mancini (“Animal-computer interaction: A manifesto”) also expressed her point of view. The article with the title “AI’s next ethical challenge: how to treat animals” can be accessed here. Today, research is also devoted to social robots. One question is how animals react to them. Human-computer interaction (HCI) experts from Yale University recently looked into this topic. Another question is whether we can create social robots specifically for animals. The first beginnings were made with toys and automatic feeders for pets. Could a social robot replace a contact person for weeks on end? What features should it have? In this context, we must pay attention to animal welfare from the outset. Some animals will love the new freedom, others will hate it.
Billions of Trees, Planted by Drones
Flash Forest, a Canadian start-up, plans to plant 40,000 trees in the north of Toronto within a few days. It uses drones, i.e. technology that also plays a role in detecting and fighting forest fires. By 2028, it aims to have planted a full 1 billion trees. “The company, like a handful of other startups that are also using tree-planting drones, believes that technology can help the world reach ambitious goals to restore forests to stem biodiversity loss and fight climate change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change says that it’s necessary to plant 1 billion hectares of trees – a forest roughly the size of the entire United States – to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.” (Fast Company, 15 May 2020) It is without doubt a good idea to use drones for planting. But you have to remember that unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) of this type have a bad energy balance. Above all, however, birds and other creatures must not be frightened away and must not be hurt (see, e.g., this article). In this context, insights from animal-machine interaction and machine ethics can be used.
Dogs Obey Social Robots
The field of animal-machine interaction is gaining new research topics with social robots. Meiying Qin from Yale University and her co-authors have brought together a Nao and a dog. From the abstract of their paper: “In two experiments, we investigate whether dogs respond to a social robot after the robot called their names, and whether dogs follow the ‘sit’ commands given by the robot. We conducted a between-subjects study (n = 34) to compare dogs’ reactions to a social robot with a loudspeaker. Results indicate that dogs gazed at the robot more often after the robot called their names than after the loudspeaker called their names. Dogs followed the ‘sit’ commands more often given by the robot than given by the loudspeaker. The contribution of this study is that it is the first study to provide preliminary evidence that 1) dogs showed positive behaviors to social robots and that 2) social robots could influence dog’s behaviors. This study enhance the understanding of the nature of the social interactions between humans and social robots from the evolutionary approach. Possible explanations for the observed behavior might point toward dogs perceiving robots as agents, the embodiment of the robot creating pressure for socialized responses, or the multimodal (i.e., verbal and visual) cues provided by the robot being more attractive than our control condition.” (Abstract) You can read the full paper via dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3371382.3380734.
Moral and Immoral Machines
Since 2012, Oliver Bendel has invented 13 artifacts of machine ethics. Nine of them have actually been implemented, including LADYBIRD, the animal-friendly vacuum cleaning robot, and LIEBOT, the chatbot that can systematically lie. Both of them have achieved a certain popularity. The information and machine ethicist is convinced that ethics does not necessarily have to produce the good. It should explore the good and the evil and, like any science, serve to gain knowledge. Accordingly, he builds both moral and immoral machines. But the immoral ones he keeps in his laboratory. In 2020, if the project is accepted, HUGGIE will see the light of day. The project idea is to create a social robot that contributes directly to a good life and economic success by touching and hugging people and especially customers. HUGGIE should be able to warm up in some places, and it should be possible to change the materials it is covered with. A research question will be: What are the possibilities besides warmth and softness? Are optical stimuli (also on displays), vibrations, noises, voices etc. important for a successful hug? All moral and immoral machines that have been created between 2012 and 2020 are compiled in a new illustration, which is shown here for the first time.
Another Animal-friendly Machine
Between June 2019 and January 2020 the project HAPPY HEDGEHOG (HHH) was implemented at the School of Business FHNW. Initiator and client was Oliver Bendel. In the context of machine ethics, the students Emanuel Graf, Kevin Bollier, Michel Beugger and Vay Lien Chang developed the prototype of a lawnmower robot that stops working as soon as it discovers a hedgehog. HHH has a thermal imaging camera. If it encounters a warm object, it further examines it using image recognition. At night a lamp mounted on top helps. After training with hundreds of photos, HHH can identify a hedgehog quite accurately. Firstly, another moral machine has been created in the laboratory, and secondly, the team provides a possible solution to a problem that frequently occurs in practice: commercial lawnmower robots often kill baby hedgehogs in the dark. HAPPY HEDGEHOG could help save them. The video on youtu.be/ijIQ8lBygME shows it without casing; a photo with casing can be found here. The robot is in the tradition of LADYBIRD, another animal-friendly machine.