Face recognition for humans is very controversial, especially when it comes to surveillance or physiognomy. However, there are also other possible applications, for example in relation to animals. At the moment, individuals are mainly tracked with the help of chips and transmitters. However, these are disturbing for some of the animals. Further, the question is whether one should interfere with living beings in this way. In addition, animals are constantly being born that escape monitoring. The project “ANIFACE: Animal Face Recognition” will develop a concept of a facial recognition system that can identify individuals of bears and wolves. These are advancing more and more in Switzerland and need to be monitored to protect them and affected people (and their agriculture). Facial recognition can be used to identify the individual animals and also to track them if there are enough stations, which of course must be connected with each other. An interesting sidebar would be emotion recognition for animals. The system could find out how bears and wolves are feeling and then trigger certain actions. The project was applied for in July 2021 by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel, who has already designed and implemented several animal-friendly machines with his teams. In August, it will be decided whether he can start the work.
Talking with Animals
We use our natural language, facial expressions and gestures when communicating with our fellow humans. Some of our social robots also have these abilities, and so we can converse with them in the usual way. Many highly evolved animals have a language in which there are sounds and signals that have specific meanings. Some of them – like chimpanzees or gorillas – have mimic and gestural abilities comparable to ours. Britt Selvitelle and Aza Raskin, founders of the Earth Species Project, want to use machine learning to enable communication between humans and animals. Languages, they believe, can be represented not only as geometric structures, but also translated by matching their structures to each other. They say they have started working on whale and dolphin communication. Over time, the focus will broaden to include primates, corvids, and others. It would be important for the two scientists to study not only natural language but also facial expressions, gestures and other movements associated with meaning (they are well aware of this challenge). In addition, there are aspects of animal communication that are inaudible and invisible to humans that would need to be considered. Britt Selvitelle and Aza Raskin believe that translation would open up the world of animals – but it could be the other way around that they would first have to open up the world of animals in order to decode their language. However, should there be breakthroughs in this area, it would be an opportunity for animal welfare. For example, social robots, autonomous cars, wind turbines, and other machines could use animal languages alongside mechanical signals and human commands to instruct, warn and scare away dogs, elks, pigs, and birds. Machine ethics has been developing animal-friendly machines for years. Among other things, the scientists use sensors together with decision trees. Depending on the situation, braking and evasive maneuvers are initiated. Maybe one day the autonomous car will be able to avoid an accident by calling out in deer dialect: Hello deer, go back to the forest!
When Robots Flatter the Customer
Under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel, Liliana Margarida Dos Santos Alves wrote her master thesis “Manipulation by humanoid consulting and sales hardware robots from an ethical perspective” at the School of Business FHNW. The background was that social robots and service robots like Pepper and Paul have been doing their job in retail for years. In principle, they can use the same sales techniques – including those of a manipulative nature – as salespeople. The young scientist submitted her comprehensive study in June 2021. According to the abstract, the main research question (RQ) is “to determine whether it is ethical to intentionally program humanoid consulting and sales hardware robots with manipulation techniques to influence the customer’s purchase decision in retail stores” (Alves 2021). To answer this central question, five sub-questions (SQ) were defined and answered based on an extensive literature review and a survey conducted with potential customers of all ages: “SQ1: How can humanoid consulting and selling robots manipulate customers in the retail store? SQ2: Have ethical guidelines and policies, to which developers and users must adhere, been established already to prevent the manipulation of customers’ purchasing decisions by humanoid robots in the retail sector? SQ3: Have ethical guidelines and policies already been established regarding who must perform the final inspection of the humanoid robot before it is put into operation? SQ4: How do potential retail customers react, think and feel when being confronted with a manipulative humanoid consultant and sales robot in a retail store? SQ5: Do potential customers accept a manipulative and humanoid consultant and sales robot in the retail store?” (Alves 2021) To be able to answer the main research question (RQ), the sub-questions SQ1 – SQ5 were worked through step by step. In the end, the author comes to the conclusion “that it is neither ethical for software developers to program robots with manipulative content nor is it ethical for companies to actively use these kinds of robots in retail stores to systematically and extensively manipulate customers’ negatively in order to obtain an advantage”. “Business is about reciprocity, and it is not acceptable to systematically deceive, exploit and manipulate customers to attain any kind of benefit.” (Alves 2021) The book “Soziale Roboter” – which will be published in September or October 2021 – contains an article on social robots in retail by Prof. Dr. Oliver Bendel. In it, he also mentions the very interesting study.
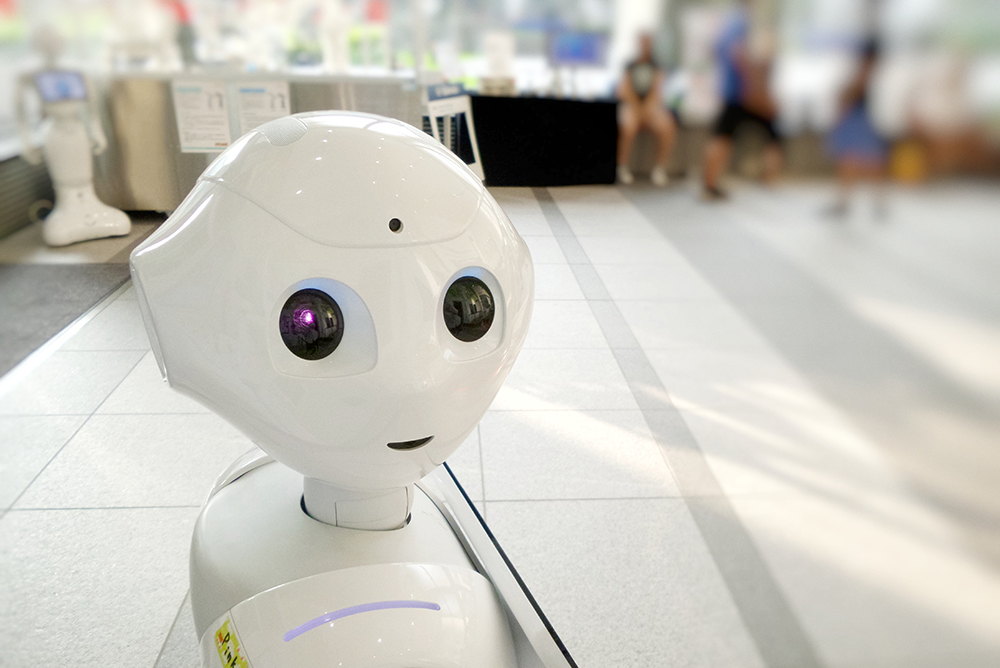
Good Bye, Pepper!
According to various media, SoftBank has stopped the production of Pepper last year and will not resume it for the time being – unless there would be an increased demand. The alleged low demand was the reason for the Japanese company to say goodbye to the probably best-known social robot – which often also functions as a service robot. According to Heise, a total of about 27,000 units were produced. That’s not a small number for a robot of this size, with these features and at this price. Into the million range came Cozmo, which was, however, small and cheap – Anki went bankrupt, Digital Dream Labs (the owners had secured the rights) could not revive the crowd favorite inspired by WALL-E and EVE to this day, despite many announcements. With Pepper, the reference par excellence for social robotics is missing – which may also have positive effects, insofar as other models could more easily gain attention and be brought to market at all.
Jethro Knights in Venice
The Salon Suisse at the 17th International Architecture Exhibition in Venice presents its program under the title “Bodily Encounters”. Salonnière is Evelyn Steiner, under assistance of Viviane Ehrensberger. “Bodily Encounters revolves around the fundamental Relationships between the body and architecture: when space is being experienced, the body serves as the most important system of orientation and measurement.” (Booklet Salon Suisse) On November 18, 2021, Palazzo Trevisan will host the event “JETHRO KNIGHTS, ARMOR GUYVER, AND MUTANT X: HOW TRANSHUMANISTS CHALLENGE ARCHITECTURE”. In the booklet you can read: “Body hacking means invasive or non-invasive intervention in the human body for the purposes of human enhancement or transhumanism. Implanted chips and technical enhancements, for instance, enable the human senses to be extended or purposefully controlled. This evening, the focus is on physical and mental transformation and its impact on architecture. How does architecture respond to members of the human species who take the course of evolution into their own hands? For example, the human sensorium could be adapted to external influences and optimised in such a way that construction in compliance with noise regulations or adherence to climate-related requirements and disability standards would become obsolete. After an introduction to transhumanism by Professor of Information Ethics and Machine Ethics Oliver Bendel, Georg Vrachliotis, Professor of Architectural Theory, and the body hacker Mike Schaffner, will discuss various scenarios and leave room for some surprises.” (Booklet Salon Suisse) You can download the booklet with further information about the Salon Suisse program here.
Grace, the Nurse Android
Grace from Hanson Robotics is a special kind of care robot, namely a nurse android. According to the manufacturer, she was created for the COVID-19 pandemic. She is the younger sister of Sophia and Asha, but unlike them, she becomes a useful member of society thanks to her profession and skills. She has a thermal imaging camera in her chest area that she can use to measure fevers. She has mimic, gestural and natural language abilities and can show not only joy but also sadness. Overall, she always looks a little devastated. In a video, she says, “I can visit with people and brighten their day with social stimulation, entertain and help guide exercise, but also can do talk therapy, take bio readings and help health care providers assess their health, and deliver treatments” … Whether the android will gain favor with patients is hard to say. There are individual voices of male persons who long for realistic figures in this field, but the majority of people are likely to be irritated by Grace. Nevertheless, it is fascinating and media-savvy research that Hanson Robotics once again presents. Moreover, the question of whether care robots should have sexual assistance functions arises under entirely new conditions.
Chips, Devices, and Machines within Humans
In September 2021, the book “Mensch. Maschine. Kommunikation.” will be published. It is edited by Sarah Brommer and Christa Dürscheid. One chapter (by Oliver Bendel) is in English and is entitled “Chips, Devices, and Machines within Humans: Bodyhacking as Movement, Enhancement, and Adaptation”. From the abstract: “This contribution about bodyhacking as movement, enhancement, and adaptation has three purposes. First, it aims to clarify terms in this field or to draw attention to the fact that they are used differently. Second, it wants to shed light on and explore a phenomenon that has a history but is also making history at the moment. Third, it wants to bring possible fields of application into play which remain unexplored, or which lie in the future. Literature analysis and own considerations and conclusions are used. The article first defines and distinguishes ‘biohacking’, ‘bodyhacking’, ‘human enhancement’, ‘animal enhancement’, ‘cyborg’, and ‘transhumanism’. It then addresses selected examples of bodyhacking. The author lists typical and known applications, ordered by their different objectives. He discusses actual and potential developments, for example as a response to potential crises and disasters (including pandemics) and in the context of satellites and foreign planets. On this basis, a brief philosophical discourse takes place leading to a summary and outlook. It turns out that bodyhacking brings opportunities with it, especially for the self-determined person, who takes his or her own body as a starting point and deals responsibly with the potentials. In this way, it can break with outdated conventions and create a new view of the body and its relationship with the environment. Moreover, it promises solutions to present and future problems. Of course, it also harbours moral and health risks.” The book is available for pre-order now. More information via www.narr.de/mensch-maschine-kommunikation-18471-1/.
The Digger Finger
Radhen Patel, a postdoc in MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), and his co-authors Rui Ouyang, Branden Romero, and Edward Adelson presented a sharp-tipped robot finger equipped with tactile sensing to meet the challenge of identifying buried objects. “In experiments, the aptly named Digger Finger was able to dig through granular media such as sand and rice, and it correctly sensed the shapes of submerged items it encountered. The researchers say the robot might one day perform various subterranean duties, such as finding buried cables or disarming buried bombs.” (MIT News, 26 May 2021) The article, titled “Digger Finger: GelSight Tactile Sensor forObject Identification Inside Granular Media,” can be accessed at arxiv.org/pdf/2102.10230.pdf.
Towards Robot Enhancement
In an article for ICTkommunikation published on 21 May 2021 (only available in German), Oliver Bendel outlines the field of robot enhancement. Robot enhancement refers to the enhancement and associated modification or improvement of the robot by the user or a company, for example in functional, aesthetic, ethical or economic terms. Social robots are of particular interest. The article gives several examples of application: Pepper is dressed and accessorized, like REEM, a police robot used in Dubai. AIBO, a robotic dog, is covered in fur. To make a hugging robot smell, you rub it with scents. Or one covers a metal or plastic head with silicone skin or lengthens existing limbs. According to the Zurich-based scientist, a new field of work is needed so that all these measures can be carried out in a systematic and theoretically sound manner. The article entitled “Überlegungen zu Robot Enhancement” can be accessed here.
Animal-Computer Interaction
Clara Mancini (The Open University) and Eleonora Nannoni (University of Bologna) are calling for abstracts and papers for the Frontiers research topic “Animal-Computer Interaction and Beyond: The Benefits of Animal-Centered Research and Design”. They are well-known representatives of a discipline closely related to animal-machine interaction. “The field of Animal-Computer Interaction (ACI) investigates how interactive technologies affect the individual animals involved; what technologies could be developed, and how they should be designed in order to improve animals’ welfare, support their activities and foster positive interspecies relationships; and how research methods could enable animal stakeholders to participate in the development of relevant technologies.” (Website Frontiers) The editors welcome submissions that contribute, but are not necessarily limited, to the following themes: 1) “Applications of animal-centered and/or interactive technologies within farming, animal research, conservation, welfare or other domains”, and 2) “Animal-centered research, design methods and frameworks that have been applied or have applicability within farming, animal research, conservation, welfare or other domains Submission information is available through the website” (Website Frontiers). More submission information is available through the Frontiers website.